“The most important thing in communication is to hear what isn’t being said.” – Peter Drucker.
Communication is a two-way process of transferring information from one person to another. Good communication is as important as maintaining a good and successful relationship or a successful business.
Effective communication demonstrates a synergistic way of working in a team towards to a shared goal. Communication maximises the strengths of team members to bring out their best. The leaders must facilitate and build the communication skills of their people if they are to steer a company toward success. Behind every successful business, there is efficient teamwork and behind efficient teamwork, there is strategic communication.
Organisations all over the world are spending substantial amount of resources to improve their teams communication techniques. To make the training to be successful, we have to know the behaviour and actions that are required for achieving effective communication. To know the behaviour of the team, we have to know how the team member thinks as an individual and as a group. Many of our day-to-day communication problems can be resolved by simply improving our communication.
Learn more about The Hermann Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI).
What do we mean by thinking preferences?
Let’s glance at the Whole Brain® Model below. Our thinking falls into four preference clusters that everyone has access to:
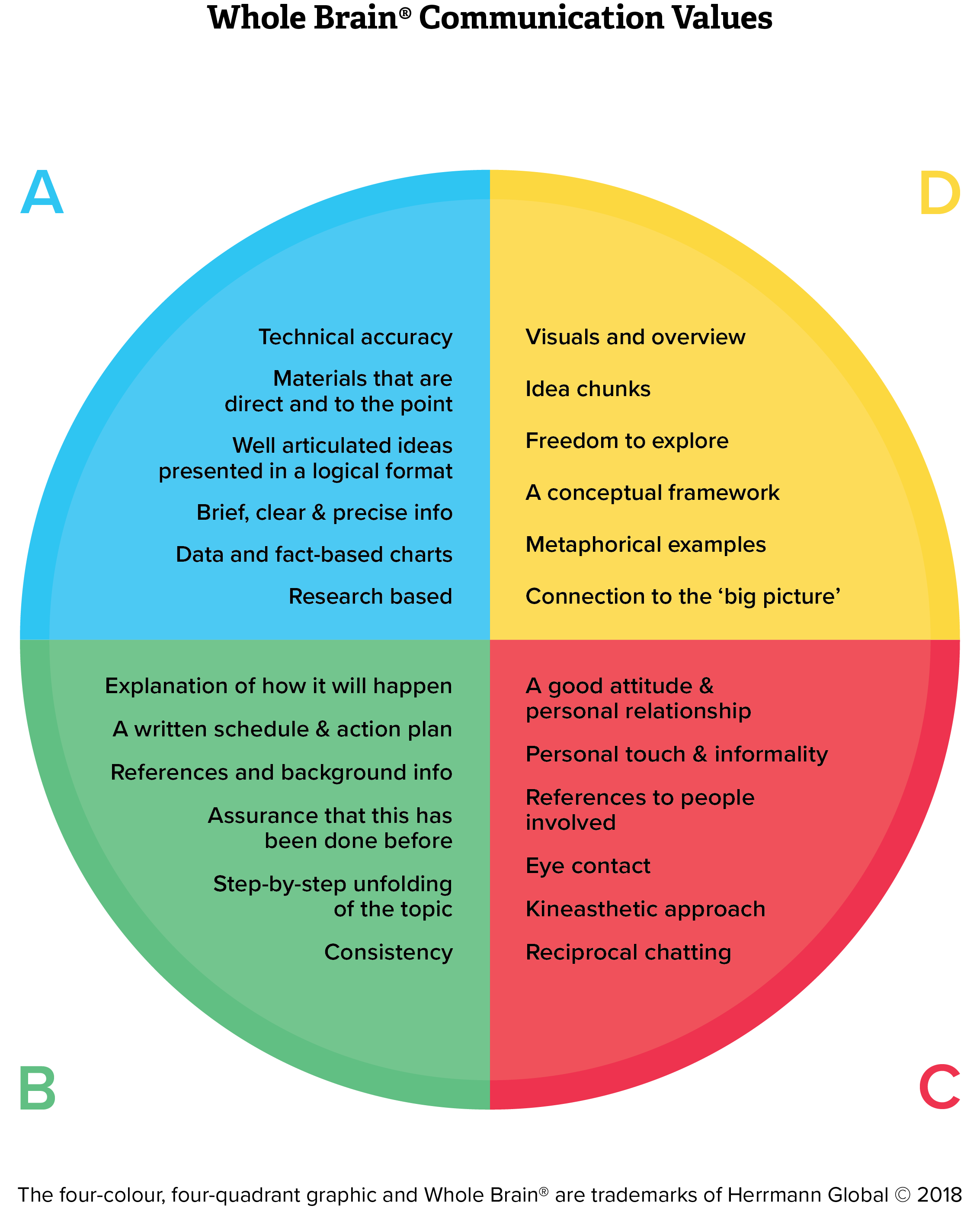
- Blue Quadrant. Logical, analytical, fact based, quantitative
- Green Quadrant. Organised, sequential, planned, detailed.
- Red Quadrant. Interpersonal, feeling based, kinesthetic, emotional.
- Yellow Quadrant. Holistic, intuitive, integrating, synthesising.
Our thinking comprised of four different thinking “selves.” All four of these are available to us, most of us, probably prefer to use some over others.
The same is true of others. When you communicate with only our own preferences in mind, we’re guaranteed to lose those who aren’t on our thinking wavelength. And if we fail to manage and integrate all the thinking in our communication, our team will be missing out on the various perspectives we need to communicate.
What is the Solution?
Think Before you Communicate. Whether we are having conversations internally or externally, it’s significantly important that we can ‘get through’ to people who have different thinking styles to our own.
- Blue Quadrant. Factual. Facts/no fluff, critical analysis, technical accuracy, goals and objectives, well-articulated ideas, brief clear, precise info, data/fact based charts.
- Green Quadrant. Plan Thorough with preferences, detailed time-action plan, step by step/ concise, in writing, in advance, rules and procedures, contingency plans, no deviating.
- Red Quadrant. Personalise. Awareness of how people feel, awareness of effects on others, listening and understanding all, open, informal discussion, expressive body and voice, intros and conversation, no hidden agendas.
- Yellow Quadrant. Visualise. Minimal details, metaphors/visuals, freedom to explore, overview/big picture, new fun, imaginative, conceptual framework, aligns with long-term strategy.
Outcome. Determine the best format for achieving that outcome.
Design. Strategise your communication with that context in mind.
Review. Evaluate your communication in order to determine which quadrant(s) are likely to create frustrations
Benefits of Strategic Communication
When Team members understand each member’s value and contribution, they can actively take part in activities that prepare the workplace to be more open and allow others to participate in varying perspectives. This process enhances the communication and coordination of employees. Another way how HBDI is more useful in strategic communication is that, when people understand peer’s HBDI, it allows members of a team to look for their ideas in such a way that they prefer to complement each other rather than having confrontation among themselves.
HBDI data yielded from the analysis of employees provides the output with detailed information representing their profile that most team members can understand. Hence, they can adjust themselves with their peers with improved communication styles as per the classification of thinking quadrants. For instance, analytical people understand charts and figures very well whereas relational people are more influenced by stories.
How can we help?
- Brief: Introduction to HBDI tool, information on Whole Brain® Model
- HBDI Assessment and going through your own HBDI individual profile
- HBDI Team Profile review
- Half-day workshop, examine the way team thinking preferences affect the way they communicate.
For more information about Whole Brain®, HBDI assessment, understanding thinking preferences, and strategic communication contact us for a detailed consultation.












