Ergonomics, also known as human factors engineering, is the scientific discipline that focuses on designing and arranging workspaces, equipment, and tasks to fit the capabilities and limitations of the human body. It aims to optimize efficiency, productivity, and safety in the workplace by reducing the risk of injuries and improving overall well-being. Organisations need to understand the consequences of hazardous manual handling tasks are not limited to physical injuries alone.
In the context of the workplace, ergonomics plays a crucial role in ensuring the health and safety of employees. By considering the physical and cognitive abilities of workers, ergonomic principles can be applied to create work environments that minimize the risk of injuries and musculoskeletal disorders. This proactive approach not only prevents workplace accidents but also enhances the overall satisfaction and productivity of employees.
Understanding the impact of hazardous manual handling tasks
Hazardous manual handling tasks involve activities that require employees to exert force, lift heavy objects, or adopt awkward postures. These tasks can significantly impact the health and safety of workers if not managed properly. Improper lifting techniques, repetitive motions, and prolonged static postures can lead to musculoskeletal disorders, chronic pain, and long-term disabilities.
The consequences of hazardous manual handling tasks are not limited to physical injuries alone. Employees who regularly engage in such activities may experience increased levels of stress, reduced job satisfaction, and decreased productivity. It is essential for organizations to recognize and address the impact of these tasks to ensure the well-being of their workforce.
The benefits of implementing ergonomic practices in the workplace
Implementing ergonomic practices in the workplace brings about numerous benefits for both the employees and the organization as a whole. By creating an environment that supports the physical and mental well-being of the workforce, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of workplace injuries and associated costs.
One of the key benefits of ergonomic practices is the prevention of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). By optimizing the design of workstations, tools, and equipment, employees are less likely to experience strains, sprains, and other MSDs. This leads to reduced absenteeism, lower healthcare costs, and increased productivity.
Furthermore, implementing ergonomic practices also enhances employee engagement and job satisfaction. When employees feel that their well-being is valued by the organization, they are more likely to be motivated and committed to their work. This, in turn, improves overall productivity and reduces turnover rates.
Compliance with WHS laws and regulations
Compliance with Work Health and Safety (WHS) laws and regulations is a legal and ethical responsibility for every organization. Ergonomics plays a crucial role in meeting these obligations by ensuring that the workplace is free from hazards and risks that could cause harm to employees.
WHS laws require employers to provide a safe and healthy work environment for their employees. This includes identifying and assessing ergonomic risks, implementing control measures to minimize those risks, and providing training and supervision to employees. Failure to comply with these laws not only exposes the organization to legal penalties but also puts employees at risk of injury or illness.
By integrating ergonomic practices into their operations, organizations demonstrate their commitment to WHS compliance and the well-being of their employees. This proactive approach not only protects the workforce but also fosters a positive safety culture within the organization.
Common workplace injuries and their relation to ergonomics
Workplace injuries can have severe consequences for both employees and organizations. Many of these injuries are directly related to ergonomics, highlighting the importance of addressing ergonomic risks in the workplace.
One of the most common workplace injuries is slips, trips, and falls. These accidents can occur due to poorly designed workspaces, inadequate lighting, or improper placement of equipment. By applying ergonomic principles, such as proper flooring, adequate lighting, and clear pathways, the risk of slips, trips, and falls can be significantly reduced.
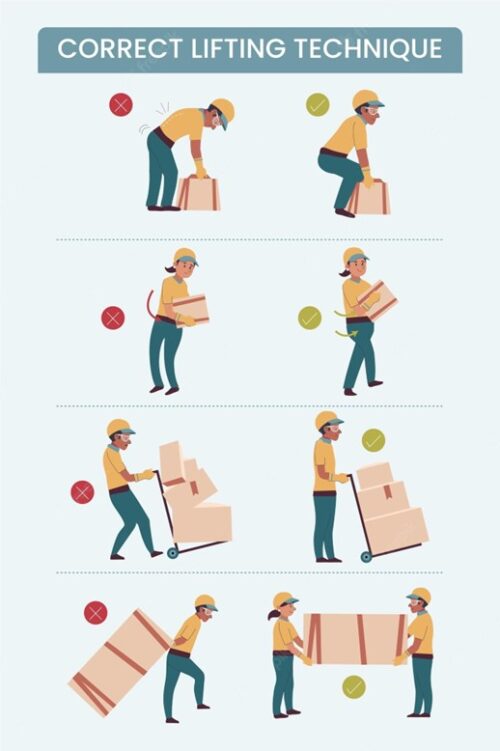
Another common workplace injury is body stressing, which encompasses injuries caused by lifting, carrying, pushing, or pulling heavy objects. These tasks can put excessive strain on the musculoskeletal system, leading to sprains, strains, and other musculoskeletal disorders. Implementing ergonomic practices, such as providing mechanical aids, training in proper lifting techniques, and adjusting workstations, can help prevent these injuries.
Identifying and assessing ergonomic risks in the workplace
To create a culture of safety, it is essential for organizations to identify and assess ergonomic risks in the workplace. This process involves evaluating the physical demands of tasks, analyzing workstations and equipment, and considering the capabilities and limitations of employees.
One effective method for identifying ergonomic risks is conducting ergonomic assessments. These assessments involve observing and analyzing work tasks, workstations, and work practices to identify potential hazards. By involving employees in the assessment process, organizations can gain valuable insights into the challenges they face and obtain buy-in for implementing ergonomic solutions.
Once ergonomic risks are identified, it is crucial to assess their significance and prioritize control measures. This involves considering factors such as the frequency and duration of exposure, the severity of potential injuries, and the feasibility of implementing control measures. By systematically addressing ergonomic risks, organizations can minimize the likelihood of workplace injuries and create a safer working environment.
Strategies to create a culture of safety through ergonomics
Creating a culture of safety requires a comprehensive approach that integrates ergonomics into all aspects of the organization. Here are some strategies to foster a culture of safety through ergonomics:
- Leadership commitment: The commitment of organizational leaders is essential in creating a culture of safety. By actively promoting and supporting ergonomic practices, leaders set the tone for the entire organization and demonstrate their commitment to the well-being of their employees.
- Employee involvement: Involving employees in the identification and resolution of ergonomic issues is crucial for creating a culture of safety. Employees have valuable insights into the challenges they face and can provide practical solutions. By engaging employees in the decision-making process, organizations empower them to take ownership of their own safety.
- Training and education: Providing training and education on work ergonomics is vital for raising awareness and building knowledge among employees. Training programs should cover topics such as proper lifting techniques, workstation setup, and the importance of taking breaks. By equipping employees with the necessary knowledge and skills, organizations empower them to make informed decisions and prevent injuries.
- Regular evaluation and improvement: Creating a culture of safety is an ongoing process that requires continuous evaluation and improvement. Regularly reviewing and updating ergonomic practices, policies, and procedures ensures that they remain effective and relevant. Organizations should also encourage feedback from employees and actively seek opportunities for improvement.
Training and education on work ergonomics
Training and education on work ergonomics are essential components of creating a culture of safety in the workplace. By equipping employees with the necessary knowledge and skills, organizations empower them to take proactive measures to prevent injuries and promote their well-being.
Work ergonomics training should cover a range of topics, including:
- Proper lifting techniques: Teaching employees how to lift objects safely and efficiently can significantly reduce the risk of strains, sprains, and other musculoskeletal disorders. This training should emphasize the importance of using leg muscles, keeping the back straight, and avoiding twisting motions.
- Workstation setup: Proper workstation setup is crucial for maintaining good posture and minimizing the risk of musculoskeletal disorders. Training should cover topics such as chair and desk height, monitor placement, keyboard and mouse positioning, and the use of ergonomic accessories.
- Importance of breaks: Encouraging employees to take regular breaks and vary their tasks is essential for preventing fatigue and reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries. Training should emphasize the importance of incorporating micro-breaks, stretching exercises, and changes in posture throughout the workday.
By providing comprehensive training and education on work ergonomics, organizations empower employees to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to protect their health and safety.
Ergonomic tools and equipment for hazardous manual handling tasks
Using ergonomic tools and equipment is crucial for managing hazardous manual handling tasks effectively. These tools and equipment are designed to reduce the physical strain on employees and minimize the risk of injuries.
Some common ergonomic tools and equipment for hazardous manual handling tasks include:
- Mechanical aids: Mechanical aids, such as lifting devices, conveyors, and powered equipment, can significantly reduce the physical effort required to perform manual handling tasks. These aids help to minimize the risk of strains, sprains, and other musculoskeletal disorders.
- Adjustable workstations: Adjustable workstations, including height-adjustable desks and chairs, allow employees to customize their work environment to fit their individual needs. This flexibility promotes good posture, reduces the risk of musculoskeletal disorders, and enhances overall comfort and well-being.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): PPE, such as back belts, knee pads, and anti-fatigue mats, can provide additional support and protection for employees engaged in hazardous manual handling tasks. These aids help to reduce the risk of injuries and promote the safe execution of tasks.
It is essential for organizations to assess the specific needs of their workforce and provide appropriate ergonomic tools and equipment to minimize the risk of injuries and promote a safe working environment.
Conclusion
Creating a culture of safety in the workplace is crucial for protecting the health and well-being of employees. Ergonomics plays a vital role in managing hazardous manual handling tasks and reducing the risk of workplace injuries. By implementing ergonomic practices, organizations can optimize work environments, minimize physical strain on employees, and enhance overall productivity.
To ensure compliance with WHS laws and regulations, organizations must identify and assess ergonomic risks, implement control measures, and provide training and education on work ergonomics. By integrating ergonomic principles into all aspects of the organization, organizations can foster a culture of safety and demonstrate their commitment to the well-being of their employees.
Contact WHS and Training Compliance Solutions for your WHS training (online, onsite and elearning) and take the first step towards creating a safer and more productive workplace.
Access Work Health and Safety Books from Amazon: Work Health and Safety