Depression is a serious mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed. This debilitating condition can impact all aspects of a person’s life, including their relationships, work, and overall well-being.
Depression is more than just feeling down or having a bad day. It is a complex disorder that involves a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors. While the exact cause of depression is still not fully understood, researchers have identified several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing this condition.
Exploring the risk factors associated with depression
Understanding the risk factors associated with depression is crucial for early intervention and prevention. By identifying these factors, individuals and healthcare professionals can take necessary steps to mitigate the risk and provide appropriate support.
The importance of early intervention for depression
Early intervention is key when it comes to managing depression. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of depression and seeking help as soon as possible can significantly improve outcomes. Studies have shown that untreated depression can lead to more severe episodes and increase the risk of suicide. By intervening early, individuals can receive the necessary support and treatment to manage their condition effectively.
Recognizing the signs of depression
Depression can manifest in various ways, and the symptoms can vary from person to person. Some common signs of depression include persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, difficulty concentrating, and thoughts of self-harm or suicide. It is important to note that not everyone with depression will experience all of these symptoms, and the severity may also differ. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is crucial to reach out for help and support.
Environmental risk factors for depression
While depression can affect anyone, certain environmental factors can increase the risk. These factors include:
Stressful life events
Experiencing significant life events such as the loss of a loved one, divorce, financial difficulties, or job loss can contribute to the development of depression. These events can disrupt one’s sense of stability and trigger emotional distress, making individuals more vulnerable to depression.
Childhood trauma
Childhood trauma, such as physical or sexual abuse, neglect, or witnessing violence, can have long-lasting effects on mental health. Studies have shown that individuals who have experienced childhood trauma are at a higher risk of developing depression later in life.
Social isolation
Lack of social support and a sense of isolation can also increase the risk of depression. People who feel disconnected from their family, friends, or community may be more susceptible to developing this condition. Loneliness can exacerbate feelings of sadness and hopelessness, making it harder to cope with depression.
Genetic risk factors for depression
Genetics also play a role in the development of depression. Research has shown that individuals with a family history of depression are more likely to experience the condition themselves. While genes alone do not determine whether someone will develop depression, they can influence an individual’s susceptibility to the disorder.
Lifestyle risk factors for depression
Certain lifestyle factors can contribute to the development of depression. These include:
Substance abuse
The misuse of drugs or alcohol can worsen symptoms of depression and increase the risk of developing the condition. Substance abuse can also interfere with the effectiveness of treatment and make it more challenging to recover.
Lack of physical activity
A sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise have been linked to an increased risk of depression. Regular physical activity can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression by releasing endorphins, which are natural mood-boosting chemicals in the brain.
Poor diet
A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats has been associated with an increased risk of depression. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall mental health and reduce the risk of depression.
Other risk factors for depression
In addition to environmental, genetic, and lifestyle factors, several other risk factors have been identified:
Gender
Women are more likely to develop depression than men. Hormonal changes during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, as well as societal and cultural factors, contribute to this gender disparity.
Chronic medical conditions
Having a chronic illness, such as diabetes, heart disease, or cancer, can increase the risk of depression. The physical and emotional challenges of living with a chronic condition can take a toll on mental health and contribute to the development of depression.
Certain medications
Some medications, such as certain types of birth control pills, corticosteroids, and beta-blockers, have been associated with an increased risk of depression as a side effect. It is important to discuss any concerns about medication and its potential effects on mental health with a healthcare provider.
Strategies for preventing and managing depression
While it may not be possible to prevent depression entirely, there are several strategies that can help reduce the risk and manage the condition effectively:
Seek professional help
Depression is a complex mental health condition that can have a profound impact on individuals’ lives. If you suspect that you or someone you know may be experiencing depression, it is essential to seek professional help. Mental health professionals can provide a proper diagnosis and develop an individualized treatment plan that may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
Build a support network
Having a strong support network of family, friends, or support groups can make a significant difference in managing depression. Surrounding yourself with understanding and compassionate individuals can provide emotional support and encouragement throughout the recovery process.
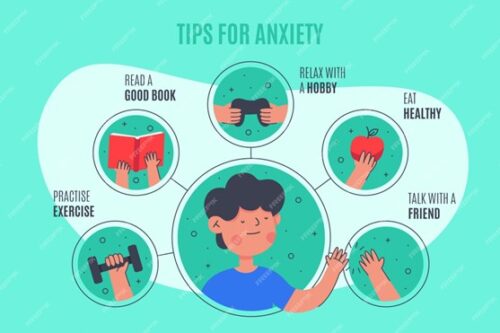
Practice self-care
Engaging in activities that promote self-care and overall well-being is crucial in managing depression. This may include practicing relaxation techniques, getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in activities that bring joy and fulfillment.
Conclusion: Shedding light on the importance of addressing risk factors for depression
Depression is a complex mental health condition that can have a profound impact on individuals’ lives. By understanding the risk factors associated with depression, early intervention can be initiated, and appropriate support can be provided. Environmental, genetic, and lifestyle factors all play a role in the development of depression, and recognizing these factors can help in prevention and management.
It is crucial to prioritize mental health and take steps to address risk factors for depression. By seeking professional help, building a support network, and practicing self-care, individuals can effectively manage depression and improve their overall well-being. Remember, if you or someone you know is experiencing signs of depression, reach out for help. Contact WHS and Training Compliance Solutions for your onsite or public MHFA training and take a step towards supporting mental health in your community.
Access Mental Health Awareness Books from Amazon: Mental Health Books